in English
post in English
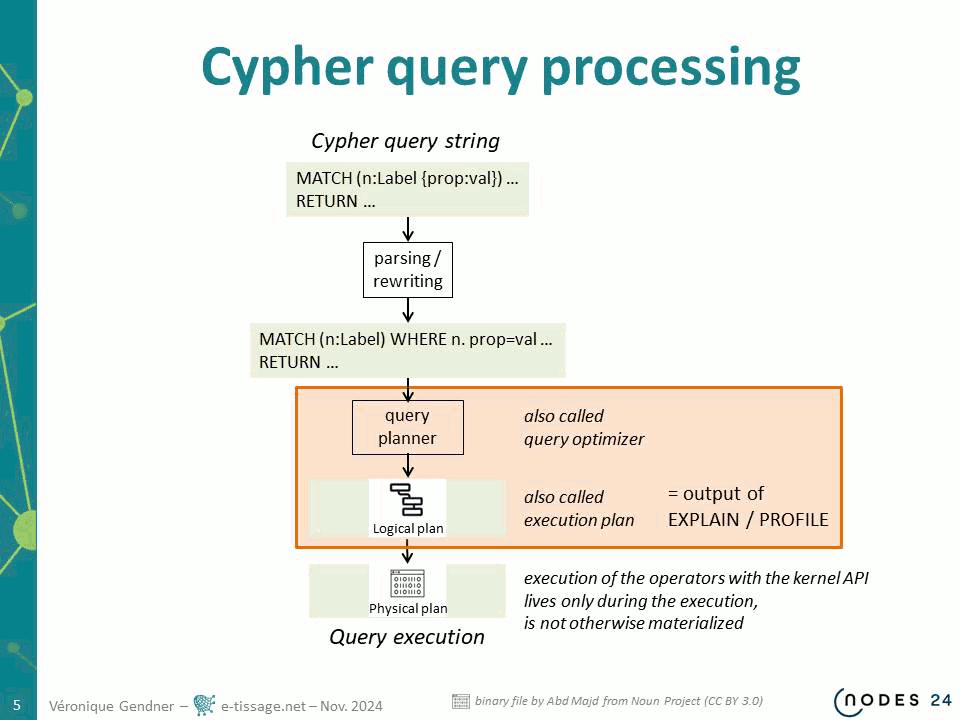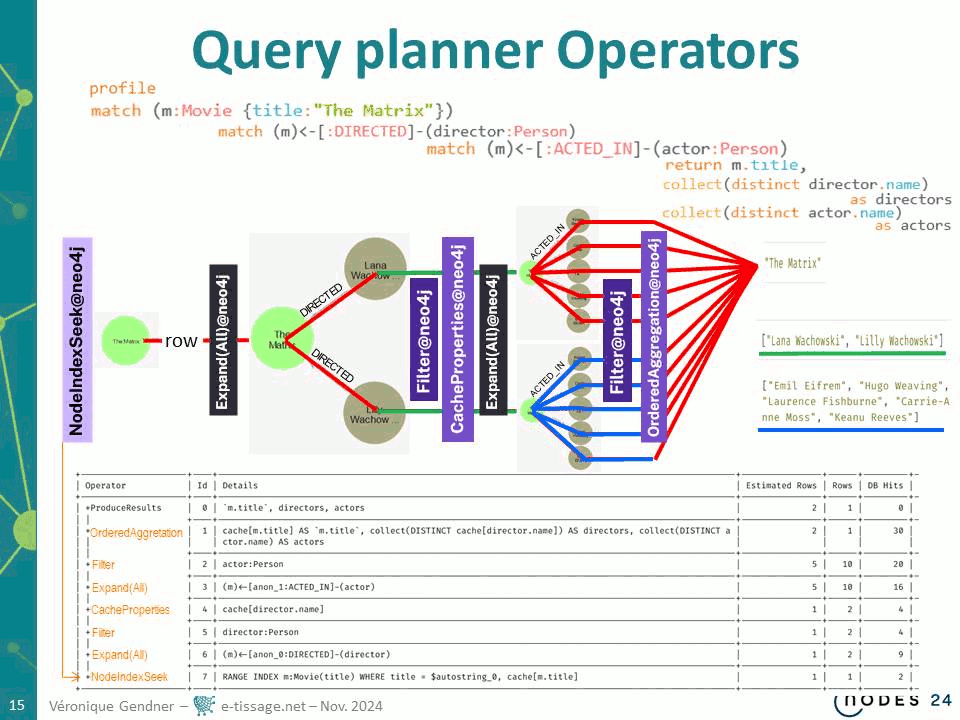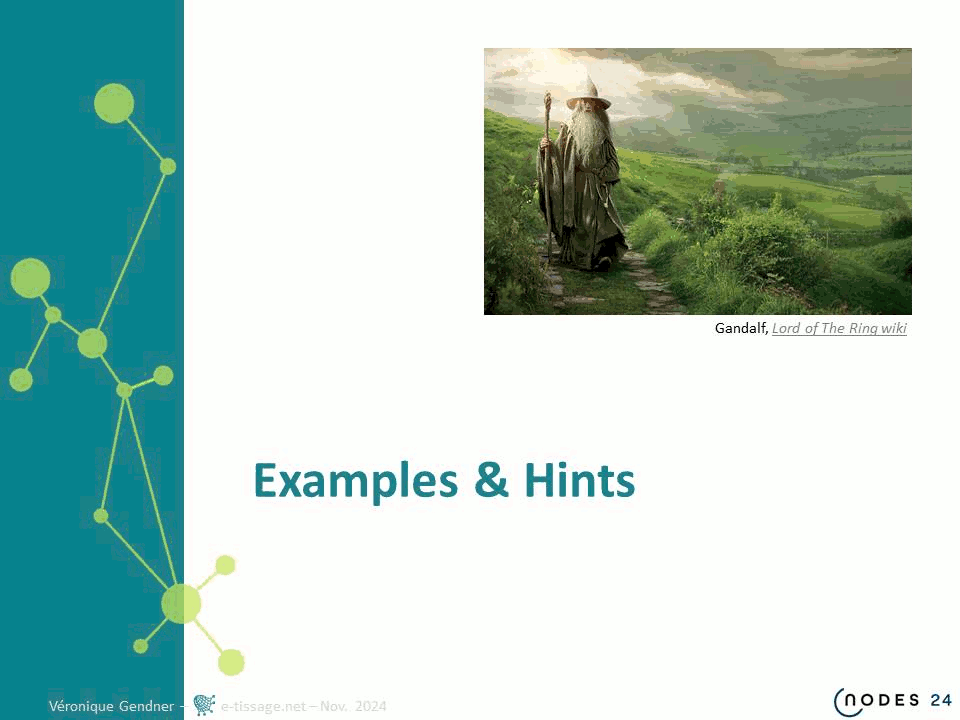
My Cypher Query Takes Too Long. What can I do ?
The purpose of this talk given at NODES 2024 is to
- give general understanding of how the cypher query planner works and the kind of things you need to know to analyses what takes times in a query processing
- give some insight on how to use EXPLAIN and PROFILE to identify what takes time in running a specific query
- give examples for you to build a better understanding of how cypher works under the hood
Fine-tuning for real time constrains or other very demanding performance constrains will NOT be addressed. This talk is for general understanding of difficulties to traverse graphs, hints about how the query planner plans query processing and some guidelines about the different parameters query processing time depends upon.
Graphs & LLM : a visual introduction
- Explore Core Concepts – Gain a foundational understanding of how graph technologies enhance Generative AI applications. Learn about essential terms and concepts such as embeddings, vector search, and Graph #RAG.
- Learn about the #Neo4j property graph model – Understand how it can be leveraged to structure and query data effectively.
- Understand Limitations and Opportunities – Identify some of the current limitations of integrating graphs with LLMs and explore opportunities for overcoming these challenges.
- Receive Practical Resources – Walk away with a cheat sheet that includes technical basics, helpful documentation, and essential resources. You’ll also receive code examples for Neo4j and #LangChain to help you get started.
Whether you’re new to the potential of combining graphs with LLMs or need to convey these ideas to non-technical colleagues, this talk will help you move forward!
Introduction To Cypher
Slides & hands-on curriculum of the Introduction to Cypher presented in Malmö, Sweden for Pink Programming
Knowledge Graph Conference demo session : Neodash
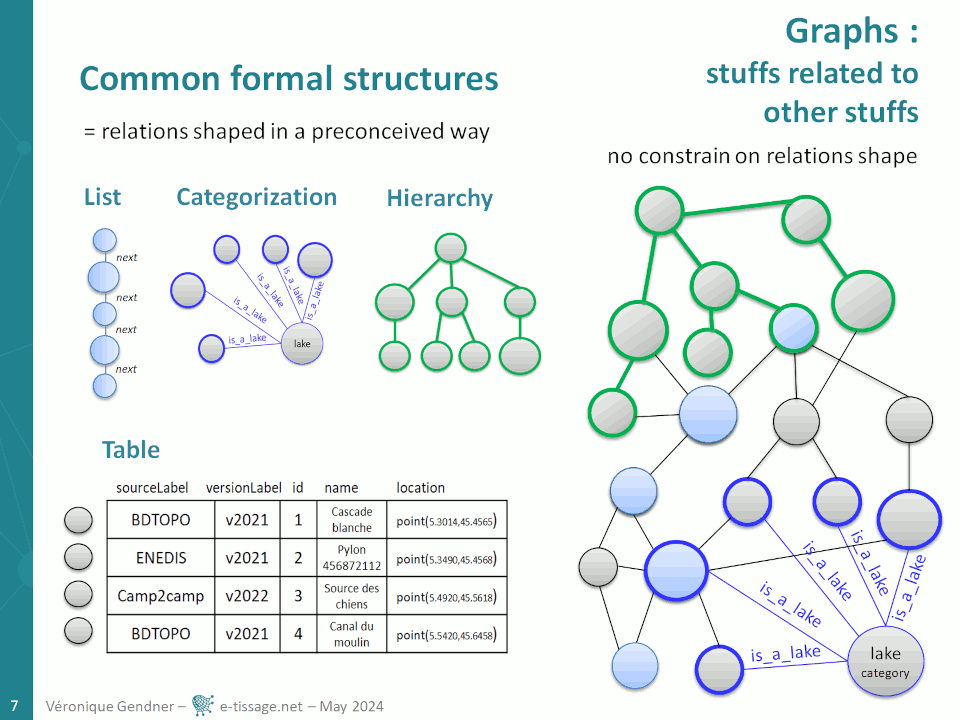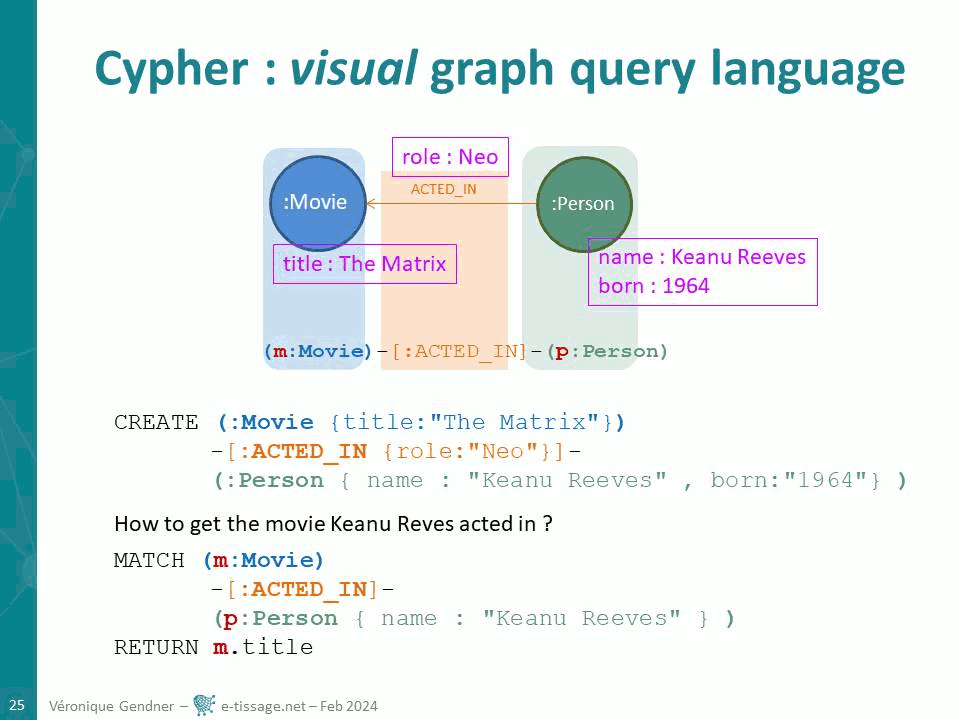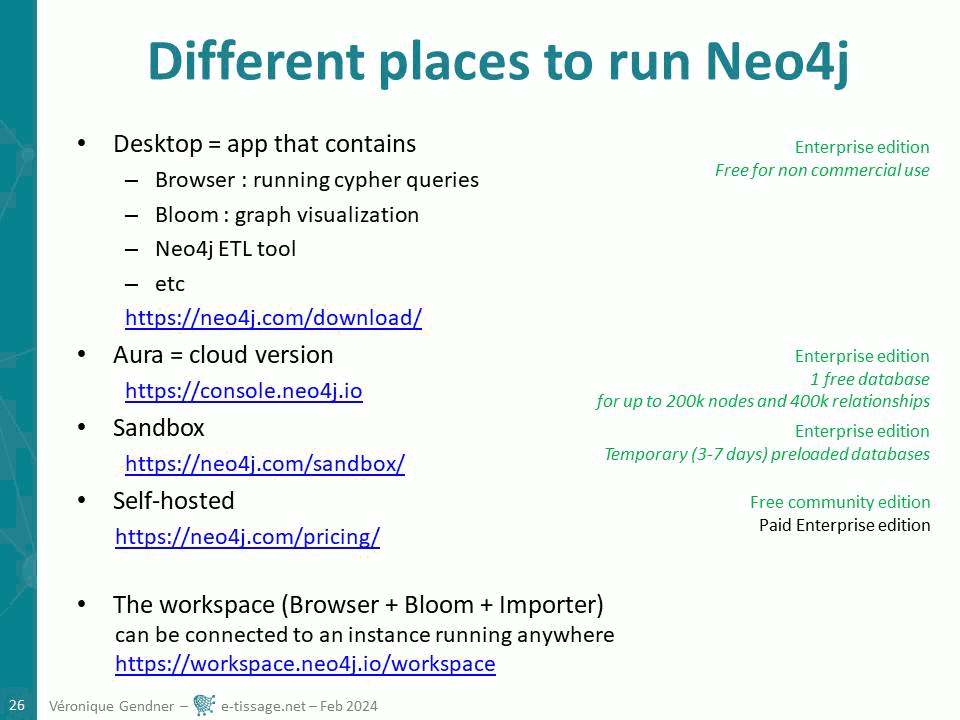
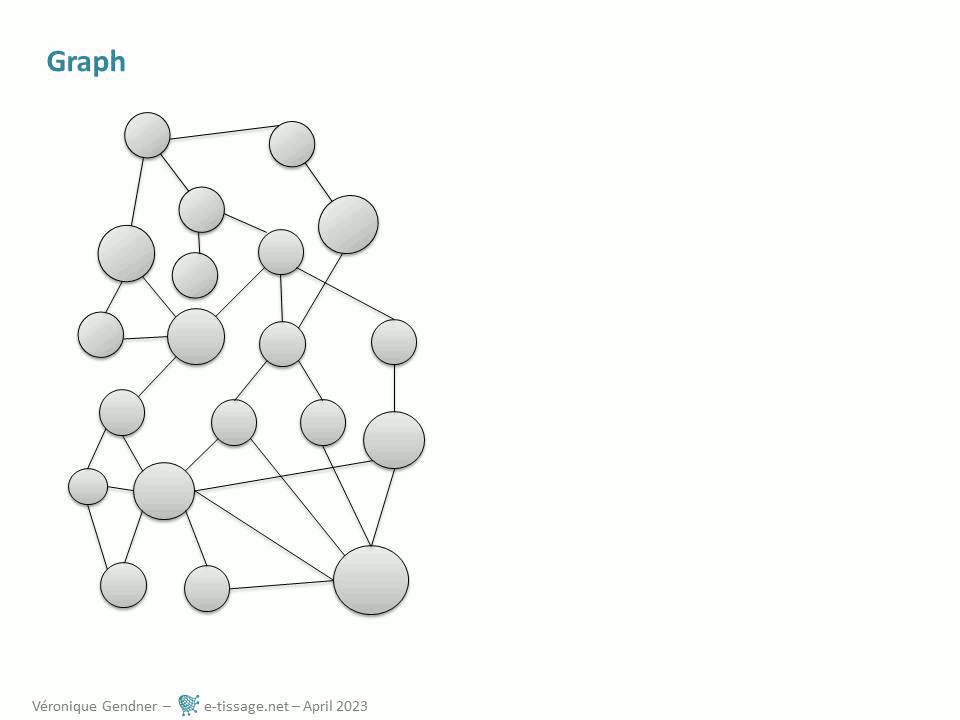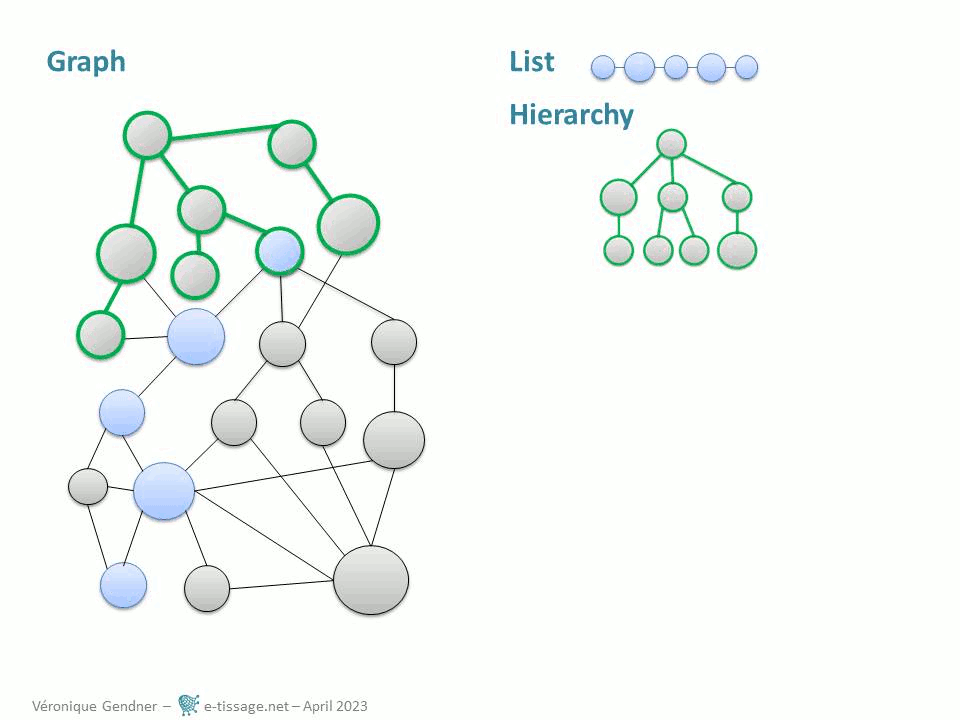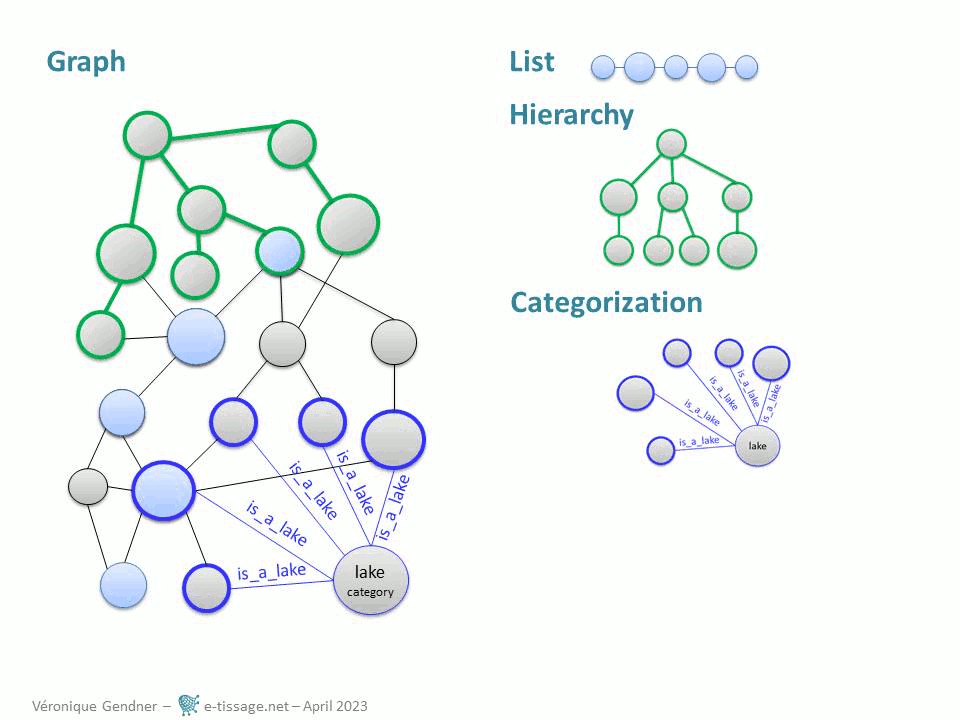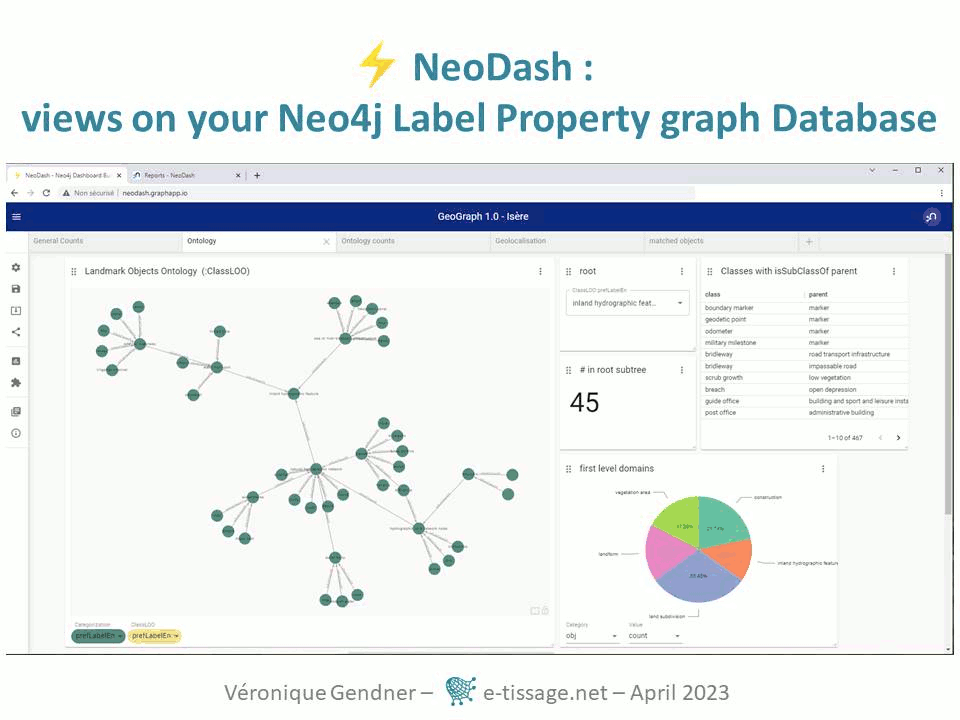
Graphs are a very useful formal structure because you can represent in one place, the precise complexity of your data, by interrelating lists, hierarchies, categorizations and tables. You can also avoid being lost in complexity by choosing what to expose for a specific purpose, in any of those more basic formal structures.
NODES 2022 : Genealogy with different graph technologies for data collection & visualization
Graphs are a very interesting structure to get the best of human thinking combined with automatic processing. Through a very intuitively graph based use case – genealogy – the following presentation at the Nodes 2022 conference takes genealogical researches as an example to illustrate possibilities that can be applied to many domain of research. It is demoing several graph issues and technologies, from data collection to visualization, including data transfer from one app to another:
- documentation collection, in a graph structure, with TheBrain Technologies application,
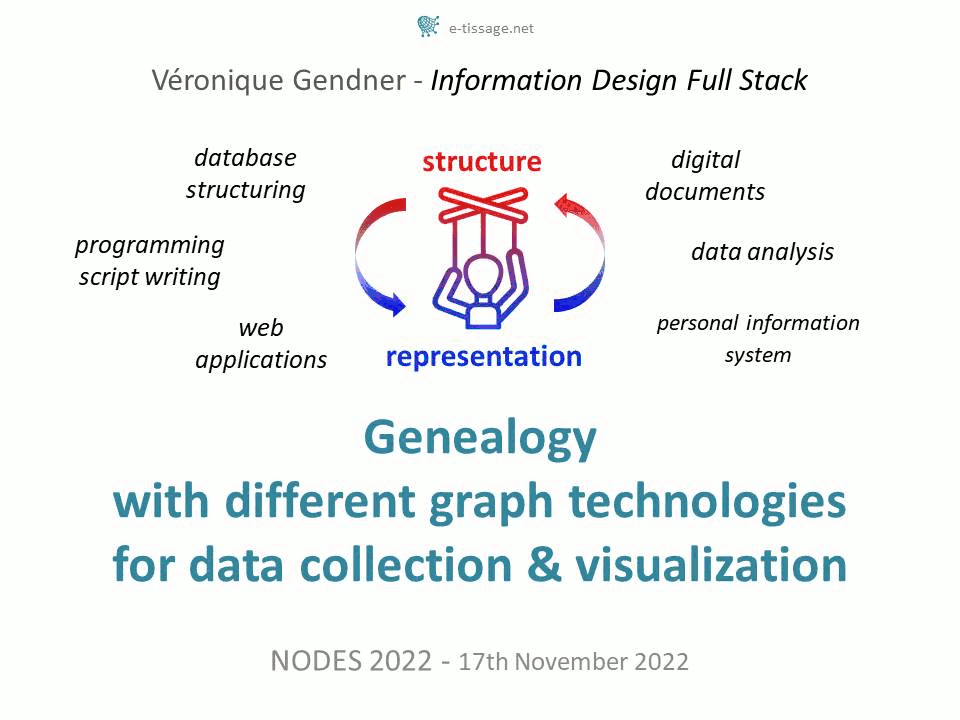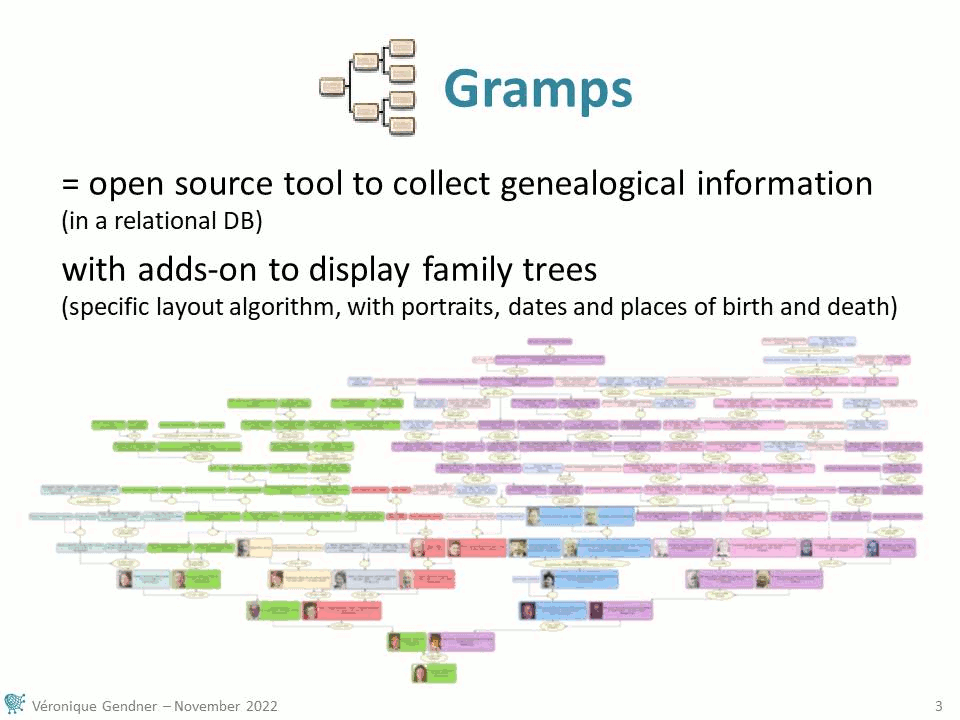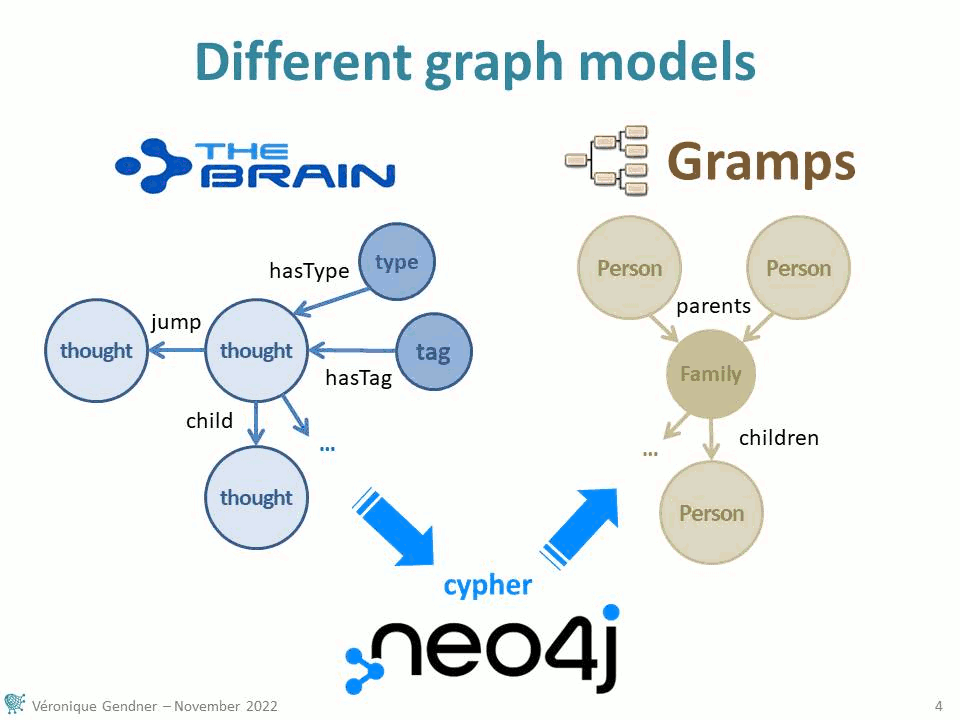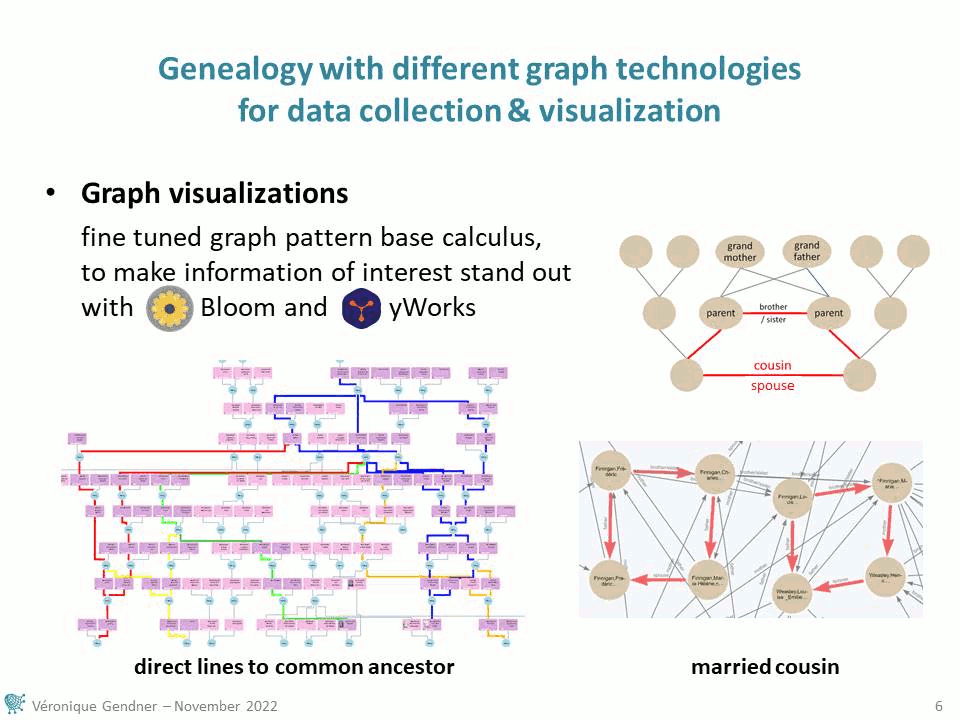
- Gramps visualizations based on a family tree specific layout algorithm
- Bloom for visual and interactive exploration of data structured in graph and
- yWorks to make precisely selected information of interest, stand out on a graph display
- as well as Neo4j graph database as a pivot technology, to make use of graph topology and graph pattern matching
Data collection and export/import process from TheBrain to Gramps via Neo4j are presented, graph models are discussed.
 alerte email - nouveaux articles
alerte email - nouveaux articles fil RSS - nouveaux articles
fil RSS - nouveaux articles Véronique Gendner, e-tissage.net
Véronique Gendner, e-tissage.net